Hemorrhoids (or hemorrhoidal disease) are vascular structures of the anal canal that incur inflammation due to changes in the mucous membrane of the last tract of the intestine and cause significant pain. The nurse is responsible for assisting the patient from the therapeutic education phase up to perioperative care.
What do hemorrhoids feel like? Characteristics of a pathology
Hemorrhoids can be defined as vascular structures of the anal canal that play a key role in maintaining fecal continence. They are a normal anatomical component of man, but their inflammation due to changes in the mucous membrane of the last intestinal tract generates a particularly painful syndrome known as haemorrhoidal disease , which is more commonly known only by the term “haemorrhoids”.
What do hemorrhoids feel like? Hemorrhoids most commonly present as purplish-red nodular structures that are extremely sensitive to touch. The factors triggering the inflammation are many and cause a thinning of the mucous wall of the rectum-anal canal with a consequent insufficiency of the haemorrhoidal veins.
Stasis, in association with the hot-humid and decidedly contaminated environment, represent the conditions that determine the mucous suffering and sometimes the sliding of the mucous and vascular structures beyond the anal orifice.
External – internal Emmorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are called internal when they remain inside while they are defined external if they come out of the anal opening making themselves visible to the naked eye.
Pathological hemorrhoids are a condition that affects 10% of the world population, with an identical incidence in both men and women. This problem develops at least once in the life of 50% of the American population, preferring the Caucasian ethnicity over the others and recording a peak in adults between 45 and 65 years of the highest social status.
The life of the affected people is terribly conditioned by this benign dysfunction which determines in the subjects an important reduction in the quality of life mainly due to the painful manifestations.
What do hemorrhoids feel like for pregnant women? Ladies in this state are a category of patients particularly affected by the disease, which negatively affects the physical, mental and social well-being of pregnant women and mothers and their clinical-assistance paths, making them even more problematic.
Hemorrhoids, symptoms and diagnosis of the pathology
The reasons leading to the development of hemorrhoidal pathology are commonly associated with:
- Family predisposition
- Pregnancy and vaginal delivery
- Age
- Incorrect feeding
- Obesity
- Excessive effort
- Sedentary life
- Contraceptive drugs
- Constipation
- Pelvic thrombosis
- Chronic liver diseases
- Sitting position for several hours
- Sports with saddle injuries (riding, cycling, motorcycling)
The patient with hemorrhoids has common symptoms which can include:
- pain and burning sensation
- bleeding
- sense of heaviness in the rectum
- mucus secretion
- anal itching
- prolapse
The diagnosis of the disease is formulated in the majority of cases following a first classic medical examination thanks to a visual examination of the anus and associated structures to which a digital and / or instrumental rectal examination can be added for the evaluation of internal and hemorrhoids. any other pathologies such as polyps and tumors of the rectum, fissures, fistulas, abscesses.
Fundamental is the evaluation and identification of haemorrhages, sometimes the cause of anemia.

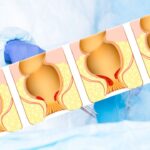
Hemorrhoids, the classification according to the level of prolapse
Hemorrhoidal disease is classified into 4 degrees depending on the level of prolapse:
- I degree : prolapse absent. Possibility of bleeding. Absence of pain in most cases
- II degree : limited prolapse at the time of defecation. Spontaneous reduction of gavoccioli
- III degree : limited prolapse at the time of defecation. Manual reduction of bobbins only
- IV degree : Complete and perennial prolapse. Total impossibility of a manual reduction of the bobbins.
Hemorrhoids, the therapeutic treatment
The treatment of hemorrhoids can be divided into 3 different types of treatment: conservative , outpatient , surgical .
Conservative treatment involves rest and the intake of NSAIDs during acute painful manifestations which are associated with a diet rich in fiber and liquids.
The application of topical drugs based on local anesthetics, zinc oxide and petroleum jelly combined with cryotherapy can be very effective especially in acute phases.
Outpatient procedures involve elastic ligation of the gavoccioli, laser therapy, selective cryotherapy and sclerotherapy, but surgical treatment in the operating room is the treatment of choice in the case of complicated and last-degree hemorrhoids, although it is associated with complications such as stenosis, infection, haemorrhages and urinary and rectal incontinence.
Surgical techniques for hemorrhoid removal
Among the main surgical techniques for haemorrhoidal disease it is possible to include:
- Milligan Morgan technique
- THD method – Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization
- Laser hemorrhoidectomy
- Hemorrhoidopexy with a circular mechanical stapler.
Hemorrhoids and patient nursing
Nursing care in haemorrhoidal pathology provides a clinical-assistance approach based on education for a non-sedentary lifestyle that includes, where possible, sport (excluding those from saddle) associated with a healthy, balanced diet rich in fibers, in order to favor the correct intestinal transit and the absorption of liquids by the body.
What do hemorrhoids feel like, and the foods to avoid
- alcohol
- sodas
- coffee
- you
- cocoa
- game
- very salty foods
- fried foods
- chocolate
- spices and chilli
- aged cheeses
- red meats and sausages.
Intimate hygiene is the basis of prevention and treatment, for this reason the nurse will instruct his clients to correctly wash the anal area with warm water and acid pH detergents, which have the function of limiting bacterial growth in an anatomical area that is decidedly sensitive to the proliferation of microorganisms.
In patients with grade III-IV hemorrhoids, surgical therapy is in some cases the only remedy to return to a normal life.
What do hemorrhoids feel like and what is the role of the nursing satff? The nurse has the task of carrying out and planning the perioperative nursing in order to guarantee the patient a correct intestinal preparation for the surgery, a comfortable and suitable positioning of the patient on the operating table and the absence of pain and post-operative complications . .
The intestinal preparation and cleansing nursing procedures provide for the administration of enemas and / or laxative solutions so that at the time of the surgical operation, generally performed under local or spinal anesthesia and in a gynecological position, the rectal ampulla is free from stool to counteract its success and favor the development of infections.
The management of post-operative pain is performed by the nursing team through the application of medical therapy with painkillers, while the patient’s comfort will be implemented by the indication to the use of aids (donuts, pillows and various supports) capable of relieving the painful symptoms due to pressure in the hypersensitive anal region.
One of the most unpleasant moments in the post-operative period is certainly that of the evacuation. For days the patient is subject to constipation and pain during and after defecation; it is in fact advisable to avoid excessive pushing actions during the same and possibly take analgesics later.
Enemas and micro-enemas in the first postoperative days are absolutely contraindicated. In the vast majority of surgeries, the surgical wounds are left open, without stitches. Precisely for this reason, especially in the vicinity of evacuation, the patient will find on the dressing of the surgical site, initially bright red blood losses, subsequently on pink-red due to the serum-blood nature of the fluids.
Monitoring for blood loss is a nursing responsibility and is helpful in avoiding anemia and other possible complications from excessive bleeding.
Careful and effective nursing, which places at the center of the project the therapeutic education of the patient to a lifestyle appropriate to his pathological condition, is able to prevent the onset of the disease and prevents the worsening of the clinical picture, allowing the patient a more rapid return to normal life, improving its quality.